Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea affects people of all ages, but it is more common in adults and the elderly, especially those who are obese. It can also affect children, often linked to health issues like enlarged tonsils and adenoids.
In this article, we will cover everything related to sleep apnea, including:
- What is sleep apnea?
- Types of sleep apnea
- Causes of OSA
- Symptoms of sleep apnea
- Diagnosis of sleep apnea
- Tips for managing OSA
What Are Tonsil Stones?
Sleep apnea (OSA) affects people of all ages, but it is more common in adults and the elderly, especially those who are obese. It can also affect children, often linked to health issues like enlarged tonsils and adenoids.
In this article, we will cover everything related to sleep apnea, including:
- Age: The risk of sleep apnea increases with age, especially in individuals over 60 years old.
- Gender: Before the age of 50, men are more likely to be affected, while after this age, the risk is equal for both genders.
- Weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for this condition.
- Health conditions: People with heart conditions, such as atrial fibrillation and heart failure, are at higher risk.
- Environmental factors: Living at high altitudes may increase the risk of certain types of sleep apnea.
Types of Sleep Apnea:
Sleep apnea can be classified into three main types based on the cause:
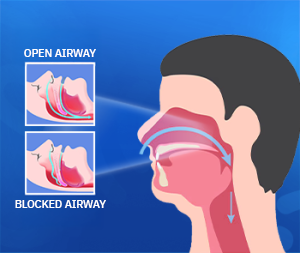
- Obstructive OSA: This is the most common type and occurs when the upper airways become blocked during sleep due to muscle relaxation in the throat. This blockage leads to temporary cessation of breathing, causing snoring and gasping, and the person may wake up suddenly feeling suffocated.
- Central sleep apnea: This is less common and occurs when the brain fails to send regular signals to the breathing muscles. It is often associated with other health problems and may not be accompanied by snoring. Central sleep apnea can affect premature infants and newborns, as it is related to changes in heart rate, low oxygen levels in the blood, and poor muscle tone.
- Complex sleep apnea syndrome (Mixed sleep apnea): This is a combination of the first two types, where there is an obstruction of the airways along with a brain signaling malfunction.
Causes of OSA:
The causes of OSA vary based on the type, and include the following:
Causes of Obstructive OSA:
- Excess weight, especially in the neck area.
- Enlarged tonsils and adenoids can obstruct the upper airway.
- Use of certain medications, such as sedatives and sleeping pills.
- Jaw deformities, such as a small or recessed jaw, affecting the airway.
- Deviated septum causing airway narrowing.
- An elongated uvula.
- Smoking and alcohol irritate the airways and increase the risk of blockage.
- Thyroid disorders can affect breathing functions.
Causes of Central OSA:
Central OSA is often a sign of serious underlying conditions such as:
- Heart diseases
- Stroke
- Neurological disorders
- Problems with the spine or brainstem injuries
Causes of Sleep Apnea During Pregnancy:
Hormonal changes during pregnancy, such as increased progesterone levels, and swelling of mucous membranes and relaxation of airway muscles, increase the risk of airway obstruction during sleep. Gaining weight during pregnancy increases pressure on the diaphragm and internal organs, narrowing the airway and making breathing harder, especially while sleeping. The growing fetus and expanding uterus exert pressure on the lungs, reducing their ability to expand and fully absorb air.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea:
Many people with OSA are unaware of their condition, as the symptoms occur during sleep and they do not remember them upon waking. Those around them may notice these symptoms more. Symptoms are divided into nighttime symptoms and daytime symptoms upon waking.
Nighttime Symptoms:
- Loud snoring
- Feeling of suffocation leading to frequent awakenings
- Insomnia and daytime fatigue
Daytime Symptoms:
Lack of restful and deep sleep results in excessive daytime sleepiness, constant fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. Affected individuals may also suffer from:
- Frequent headaches
- Dry mouth and throat
- Memory problems
- Mood changes such as depression or anxiety
Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea:
The diagnosis of sleep apnea is made through several stages. It begins with gathering the patient’s medical history and conducting a physical examination to identify factors that increase the risk of OSA. The doctor then evaluates the patient’s level of sleepiness and checks for any sleep disorders. Finally, a polysomnography test (sleep study) is conducted to monitor the brain’s electrical activity, muscle activity, and eye movements during sleep to detect any breathing disturbances.
Treatment of Sleep Apnea:
OSA symptoms can be alleviated by making some simple lifestyle changes, such as:
- Losing excess weight
- Quitting smoking
- Treating seasonal allergies
- Sleeping on the side instead of the back or stomach
If these changes do not yield the desired results, or in cases of moderate to severe sleep apnea, the doctor may recommend other treatment options, including:
- Oxygen therapy
- Medications prescribed by the doctor
- Surgery to enlarge the airway
Tips for Managing OSA:
To manage OSA effectively, follow these tips:
- Maintain a healthy weight, as this helps reduce pressure on the upper airways.
- Sleep on your side and elevate your head slightly to keep airways open.
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to maintain a healthy weight and improve overall health.
- Drink plenty of water to keep the mucous membranes in the airways hydrated.
- Regular exercise helps strengthen muscles and improves heart and lung function.
- Limit consumption of coffee, tea, alcohol, and other stimulants, especially before bed.
In conclusion, OSA is not just a sleep issue, but a sign of an underlying health problem that can affect your quality of life. Fortunately, sleep apnea can be diagnosed and treated effectively. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of sleep apnea, don’t hesitate to consult an ENT doctor. Remember, good sleep is the foundation of good health, so seek help if you face difficulties in sleeping.