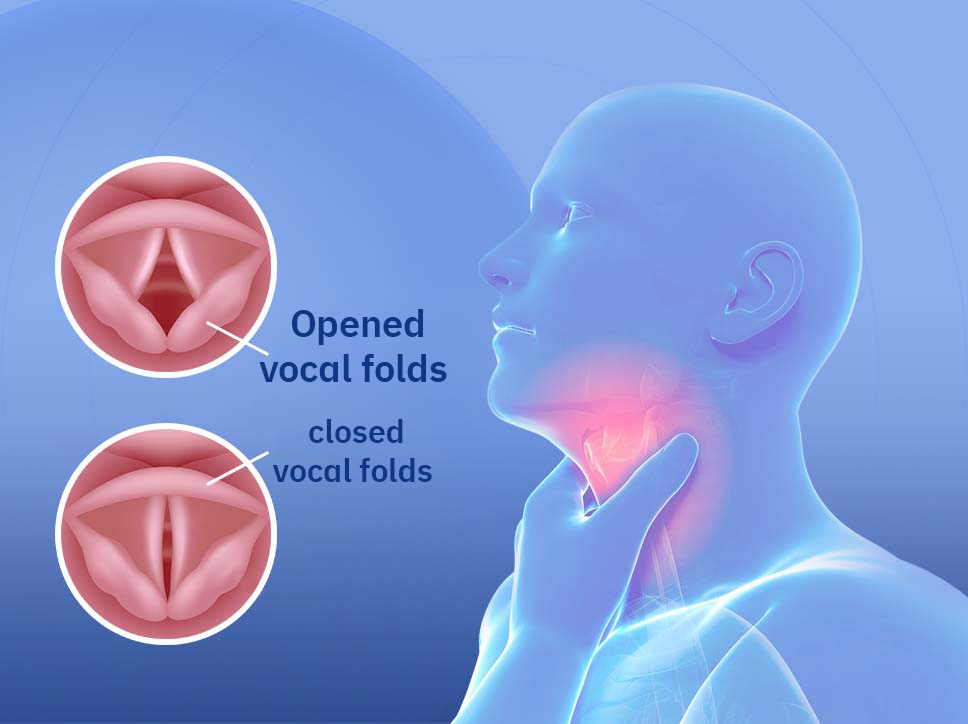
Vocal Cords
Have you ever imagined waking up to find your voice completely gone? You try to speak, but no one can hear you?!
This can happen as a result of vocal cords disorders, which may even lead to complete voice loss.
The vocal cords are two flexible bands of muscular tissue located within the larynx, just above the trachea. They are responsible for producing sound by vibrating as air passes through them during exhalation. The speed of their vibration varies depending on pitch—faster vibrations produce high-pitched sounds, while slower vibrations produce lower tones.
These cords can become inflamed due to certain conditions and factors, which we will explore throughout this article.
- Types of Vocal Cords Disorders
- Symptoms of Vocal Cords Disorders
- Causes of Vocal Cords Inflammation
- When to See an ENT Specialist
- Treatment for Vocal Cords Disorders
- Prevention Tips for Vocal Cords Inflammation
Types of Vocal Cords Disorders
1. Laryngitis
This occurs due to a viral infection affecting the vocal cords, causing them to swell. When the swollen cords vibrate, they produce a sound that differs from the person’s normal voice. In severe cases, it may lead to complete loss of voice.
2. Vocal Nodules
Also called vocal fold nodules or polyps, these are small paired growths that develop on each vocal cord due to excessive strain or overuse. They typically form in the area experiencing the most pressure during speech, especially with prolonged loud voice use—commonly seen in singers and performers.
3. Tumors (Benign and Malignant)
Benign tumors are soft, small growths that may appear singly on the vocal cords, often caused by prolonged exposure to irritants like smoke or chemical fumes.
Malignant tumors, on the other hand, are more common in smokers and individuals who consume excessive alcohol. These pose serious health risks if not detected and treated early.
4. Vocal Cord Paralysis
This condition arises when the vocal cords lose their ability to vibrate effectively. It may lead to a weak or unclear voice and allow food or liquids to slip into the windpipe, increasing the risk of choking due to improper cord closure.
Symptoms of Vocal Cords Disorders
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, and may include:
Sore throat with hoarseness and voice changes
Low vocal volume and difficulty sustaining speech
Breathy, raspy voice
Inability to coordinate breathing during speech
- Sensation of choking and difficulty swallowing or breathing
Causes of Vocal Cords Inflammation
Several factors may contribute to vocal cords inflammation, such as:
- Viral infections
- Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), which causes throat inflammation
- Long-term exposure to dust or smoke
- Prolonged loud speaking, especially in vocally demanding professions (e.g., teachers, singers)
- Disruption of nerve signals to the muscles controlling the vocal cords
- Lung or thyroid cancer
- Stroke
- Trauma to the head, neck, or chest that may affect the nerves feeding the vocal cords
- Neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis
- Genetic mutations causing abnormal cell growth leading to benign or malignant tumors—particularly common in smokers
When to See an ENT Specialist
If any of the above symptoms persist for more than two weeks, it is essential to consult an ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist. The doctor will perform thorough examinations to assess inflammation levels, determine the type of disorder, and prescribe an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment for Vocal Cords Disorders
Once diagnosed, treatment may include:
Adequate fluid intake
Voice rest and reduced use of the vocal cords
Allergy management if sensitivity to dust or fumes is involved
Prescribed anti-inflammatory or anti-reflux medications
- In some advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove non-cancerous nodules or lesions obstructing vocal cords function, restoring their normal vibration and closure ability
Prevention Tips for Vocal Cords Inflammation
To keep your vocal cords and larynx healthy:
Avoid prolonged loud speaking or shouting
If you suffer from GERD, take preventive steps such as:
Avoid lying down immediately after meals
Reduce intake of fatty foods
Quit smoking, caffeine, and alcohol
If you have viral laryngitis, cover your mouth when coughing and wash your hands regularly to prevent spreading the infection
Vocal cords disorders are common, especially among individuals whose professions demand heavy vocal use. Researchers at the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) are actively studying high-risk individuals to develop clinical strategies that reduce strain and prevent these disorders.