Earwax Blockage
Earwax blockage occurs when earwax builds up and blocks the ear canal, affecting hearing. Although earwax is the ear’s natural defense against microbes, infections, and other harmful substances, excessive accumulation can lead to this condition.
In this article, you’ll discover everything you need to know about Earwax Blockage in comprehensive detail.
- Causes of Earwax Blockage
- Symptoms of Earwax Blockage
- Diagnosis of Earwax Blockage
- Treatment for Earwax Blockage
- Complications of Earwax Blockage
- How to Prevent Earwax Blockage
Causes of Earwax Blockage:
Earwax is produced by glands in the auditory canal. When excess wax is secreted or improperly cleaned, it can accumulate and block the canal, reducing hearing ability. Earwax Blockage can affect anyone, with about 10% of children and 5% of adults experiencing it. Risk factors include:
Frequent use of earphones or hearing aids
Having excessive hair in the ears
Suffering from skin conditions like eczema
External ear infections
Use of earplugs or cotton swabs, which push wax deeper
Naturally narrow ear canals due to congenital factors or chronic inflammation
Symptoms of Earwax Blockage:
Signs that may indicate Earwax Blockage include:
Itching inside the ear
Tinnitus (ringing in the ear)
Dizziness
Ear pain
Sudden hearing loss or hearing weakness
Improper removal of wax can lead to infections or inflammation. Seek medical attention immediately if you notice:
Discharge from the ear
Complete hearing loss
Fever and coughing
Severe ear pain
Foul smell from the ear
Diagnosis of Earwax Blockage:
If left untreated, accumulated wax can obstruct the view inside the ear, making accurate diagnosis difficult. Diagnosis typically involves:
Reviewing the patient’s symptoms
Otoscopic examination to visually confirm blockage
Medical evaluation and review of the patient’s history
Treatment for Earwax Blockage:
In the absence of symptoms or actual blockage, removal may not be necessary. Treatment depends on the patient’s condition and medical history. For those experiencing:
Excessive wax production
Narrowing of the ear canal due to inflammation
Treatment options may include:
Using ear drops or glycerin to soften the wax
Irrigation with warm water to dissolve wax using a syringe to gently extract it
Complications of Earwax Blockage:
If not managed properly, Earwax Blockage may lead to:
Ear bleeding
Hearing loss
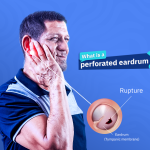
Eardrum perforation
Middle ear infections
How to Prevent Earwax Blockage:
To keep your ears safe from wax buildup, follow these tips:
Avoid using cotton swabs to clean earwax, as they stimulate the fine hairs in the ear canal, signaling glands to produce more wax
Refrain from using earplugs, especially during sleep
Do not use ear drops without consulting a doctor
- Visit an ENT specialist once a year to professionally clean accumulated wax and prevent blockage
Finally, before attempting any method to clean or treat Earwax Blockage, it is essential to consult a specialist to choose the safest and most effective approach—avoiding improper cleaning practices that could potentially harm your hearing in the short or long term.