Bat Ear
The ear is a fundamental feature of the face, and any deformity in its natural shape can significantly affect overall facial aesthetics. For some individuals, bat ear—also known as prominent ear—is a condition in which the ear protrudes abnormally from the head. While not harmful to hearing, it can impact self-confidence and emotional well-being. Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options, ranging from non-surgical interventions to advanced cosmetic surgery. In this article, we explore the causes, treatment options, and surgical approach to managing bat ear.
- What Can a Rhinoscope Detect?
- Causes of Bat Ear
- Bat Ear Treatment: Best Options Available
- Protruding Ears: Causes, Treatment Options, and the Most Effective Solutions
- Is Bat Ear Surgery Safe?
- Recovery After Bat Ear Surgery
What Is Bat Ear?
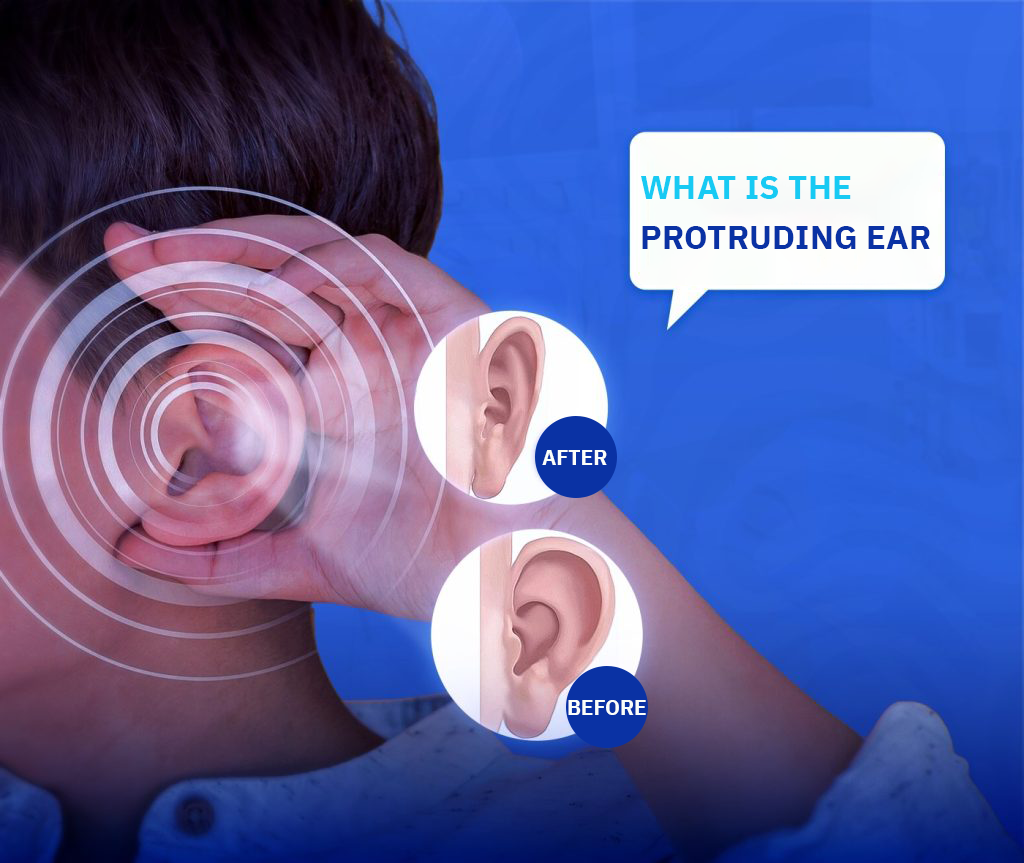
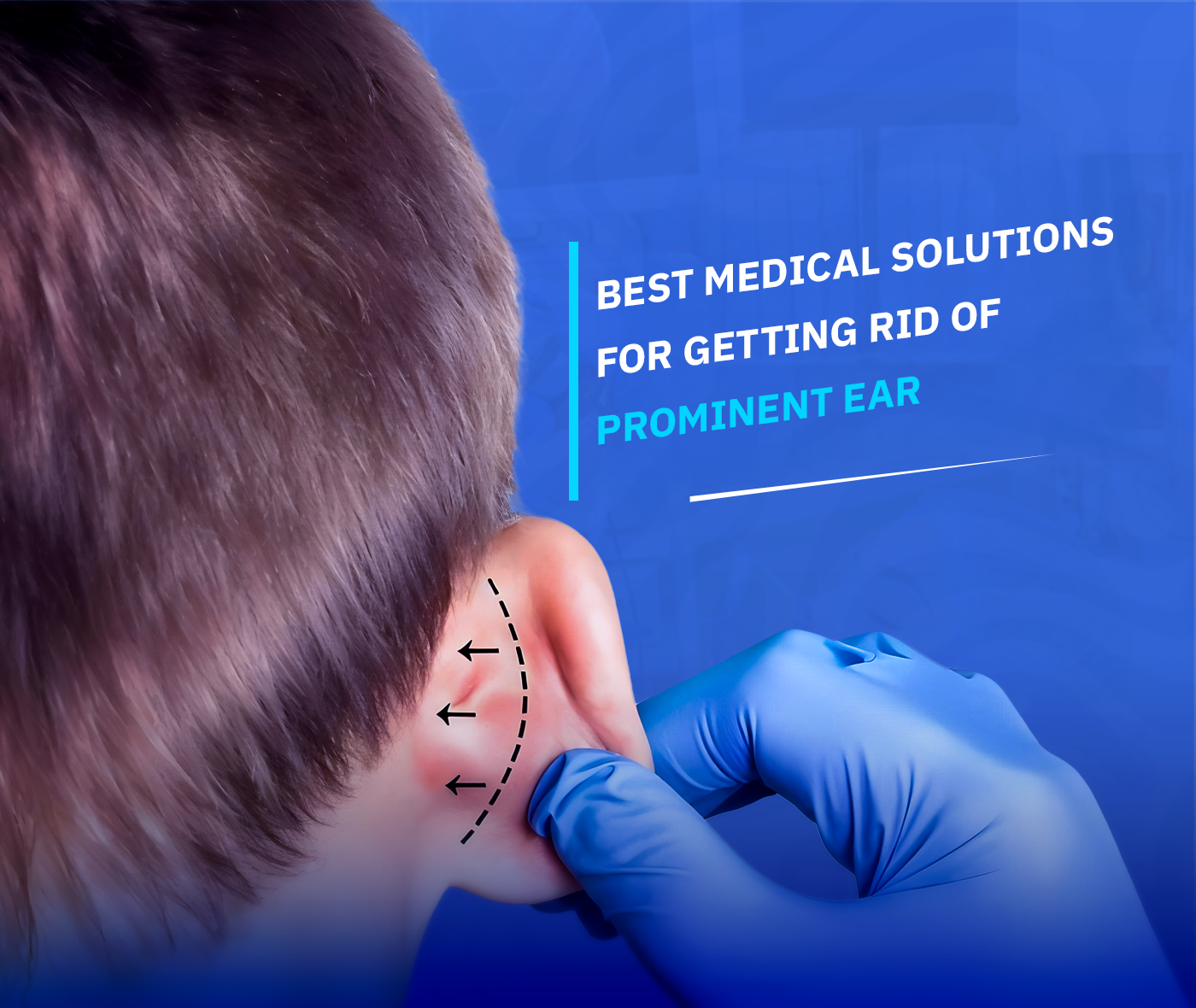
Bat ear, or prominent ear, refers to an anatomical condition where one or both ears stick out more than 2 centimeters from the side of the head, making them noticeably visible from the front. Medical statistics show that 1% to 2% of the population is born with this condition. In some cases, it may develop during early childhood.
Although bat ear does not affect hearing or the overall health of the ear, it can have psychological effects—particularly in children—leading to embarrassment or low self-esteem.
Causes of Bat Ear
Several anatomical factors can contribute to the development of bat ear:
Underdeveloped antihelical fold:
In a typical ear, the outer rim should bend inward forming a “C” shape, with a defined “Y”-shaped fold on the inside. In the case of bat ear, this folding is incomplete or absent, causing the ear to project outward.
Overgrowth of conchal cartilage:
The concha, a bowl-shaped part of the ear, may grow excessively and push the ear further away from the head, contributing to the prominent appearance.
Excessive cartilage flexibility:
Sometimes, the cartilage is overly pliable, allowing the ear to bend outward more easily and remain in an abnormal position.
Protruding Ears: Causes, Treatment Options, and the Most Effective Solutions
The appropriate treatment for bat ear depends on factors such as the patient’s age, the severity of the condition, and the psychological impact. In mild cases, especially in newborns, the condition may resolve on its own. However, if the prominence persists or affects the child’s confidence, medical intervention may be necessary.
1. Non-Surgical Treatment
In infants, early intervention using ear molding devices such as splints or ear bands can correct the ear’s shape. These methods are most effective when initiated within the first few weeks of life and may help avoid surgery altogether.
2. Surgical Treatment (Otoplasty)
If non-invasive methods are unsuccessful or if the deformity remains pronounced, otoplasty—a cosmetic surgery for ear reshaping—may be recommended. This procedure is typically performed around the age of five, when the ear is nearly fully developed.
What Is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty, also known as bat ear surgery, is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to reshape and reposition prominent ears closer to the head. The surgery involves sculpting or folding the ear cartilage and may include the removal of excess skin. It aims to create a natural, symmetrical appearance that complements the rest of the face.
The procedure generally takes about two hours and is performed under local or general anesthesia. Postoperative care includes wearing special bandages for several days and avoiding physical activities that might strain the ears.
Is Bat Ear Surgery Safe?
Bat ear correction surgery is considered safe when performed by a qualified and experienced plastic or ENT surgeon. However, like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks, including:
- Infection
- Bleeding or hematoma
- Scarring
- Temporary or permanent changes in skin sensation
- Reactions to anesthesia
These risks can be minimized through proper pre-operative assessment and adherence to post-operative instructions.
Recovery After Bat Ear Surgery
Recovery time varies between individuals depending on age, overall health, and how closely post-operative care instructions are followed. In general:
- Initial healing takes 1–2 weeks
- Full recovery may take 1–2 months
- Patients should avoid strenuous physical activity for at least 8–12 weeks
- Mild pain, swelling, or discomfort is common and manageable with prescribed medications
- Wearing a compression headband or ear support is usually advised for several weeks
Bat ear is a cosmetic condition that can impact a person’s self-image and psychological well-being. While it does not impair auditory function, its aesthetic implications often prompt individuals or caregivers to seek corrective treatment. Thanks to modern medicine, both surgical and non-surgical options are available to effectively address the issue, restore facial symmetry, and enhance self-confidence. Consultation with a qualified specialist is essential to determine the most suitable approach for each case.