Cholesteatoma (Ear Bone Erosion)
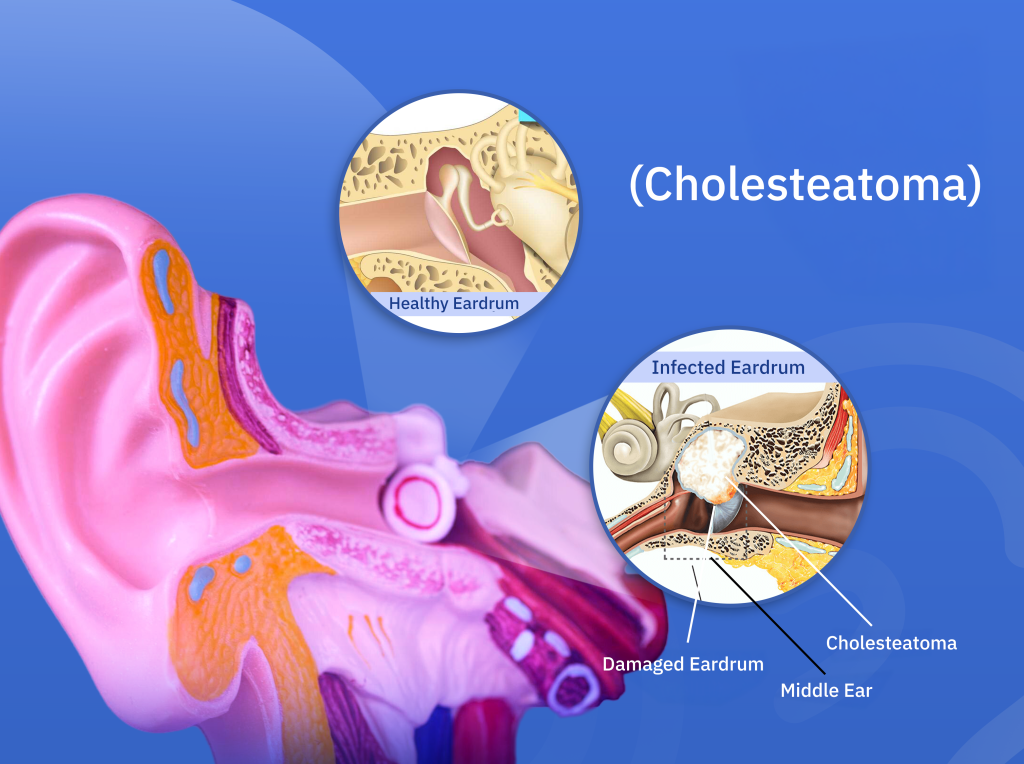
What is Cholesteatoma?
Cholesteatoma is a condition characterized by an abnormal growth of a sac-like structure in the middle ear or mastoid bone (the bone behind the ear). It is not a cancerous tumor but can cause serious complications if untreated. It typically develops due to recurrent ear infections, ear trauma, or Eustachian tube dysfunction. The sac is lined with keratinizing squamous epithelium (similar to outer skin), and as it expands, it can erode nearby structures such as the ossicles (tiny ear bones involved in hearing) or the facial nerve.
Symptoms of Cholesteatoma:
- Chronic Ear Infections: Recurrent or persistent infections that do not respond to treatment.
- Hearing Loss: Caused by impaired sound transmission due to damage to the middle ear ossicles.
- Ear Discharge: Foul-smelling drainage resulting from infection.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing sounds in the ear.
- Vertigo: May affect balance organs in the inner ear, leading to dizziness.
Diagnosis of Cholesteatoma:
If Ear Bone Erosion is suspected, consult an ENT specialist. Diagnosis involves:
- Medical History: Reviewing symptoms and health background.
- Clinical Examination: Inspecting the ear for discharge or abnormalities.
- Imaging: CT scans or MRIs to assess the extent and impact on surrounding structures.
Treatment of Cholesteatoma:
• Surgical Treatment:
- The primary treatment is surgery to remove the cholesteatoma, aiming to:
- Completely excise the sac.
- Repair damage to ear structures (e.g., ossicles).
- Prevent complications such as meningitis or facial nerve paralysis.
The surgical approach (e.g., mastoidectomy or ear reconstruction) depends on the cholesteatoma’s size and involvement of adjacent structures.
• Follow-Up:
Regular post-surgical visits to monitor healing and detect recurrence. Additional surgeries may be required in some cases.
Important Notes:
Ear Bone Erosion can be a serious condition if left untreated, potentially leading to permanent hearing loss, facial paralysis, or brain infections. Early diagnosis and prompt intervention are critical to prevent complications. If you suspect cholesteatoma, seek medical attention immediately.




