Cortisone Ear Injections
Cortisone Ear Injections: A Promising Treatment for Inner Ear Disorders
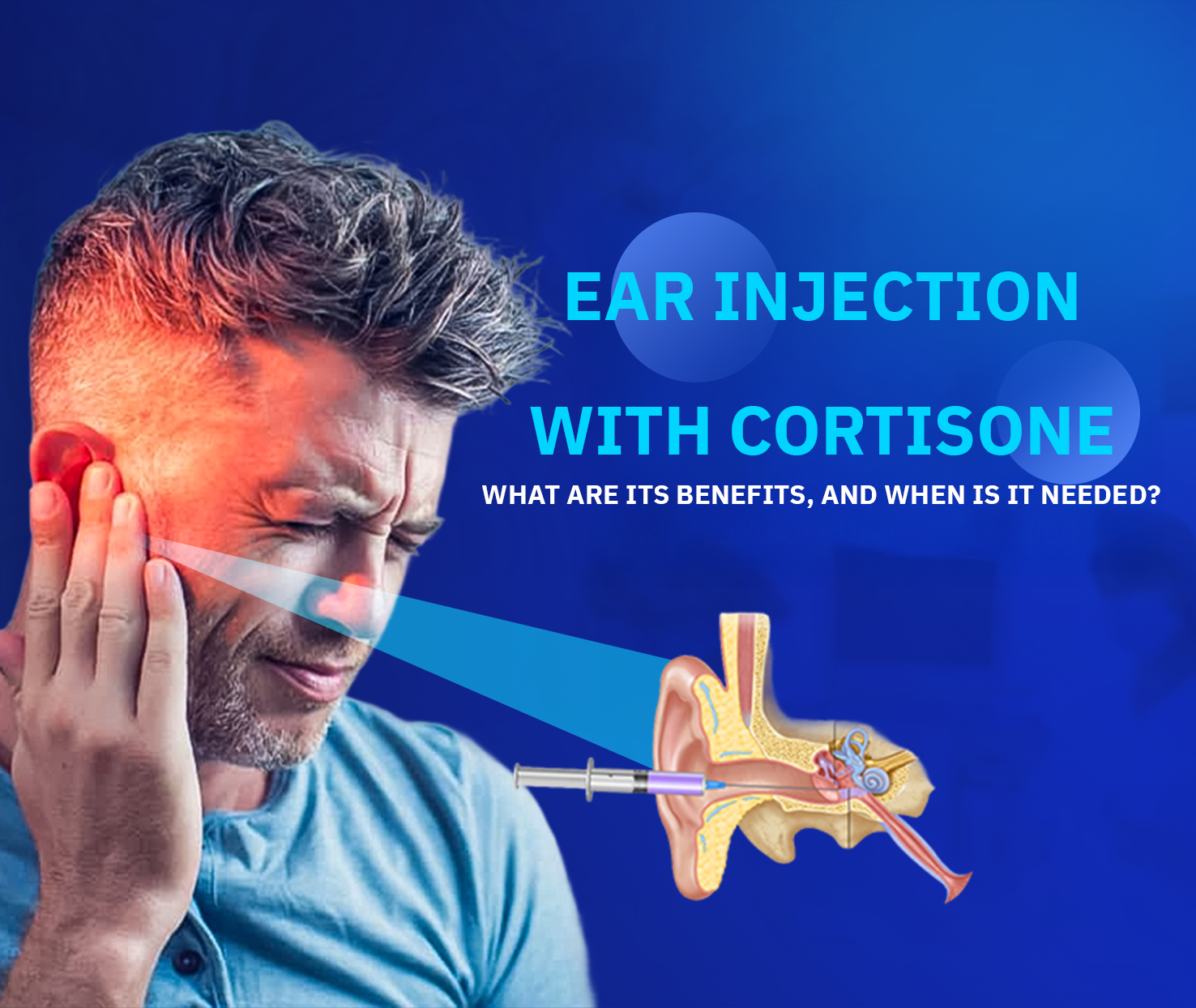
Cortisone ear injections are considered an effective therapeutic option for hearing loss caused by inner ear disorders. They also have medical benefits in alleviating tinnitus and vertigo associated with these conditions. Cortisone is available in various forms, such as oral tablets, intravenous injections, and tympanic membrane (eardrum) injections.
One of the advantages of tympanic cortisone injections is their ability to deliver the medication directly to the middle ear, where it passes through the round window membrane into the inner ear, thereby accelerating the healing process. In this article, we will explore the steps involved in cortisone ear injections and the benefits they offer.

- Benefits of Cortisone Ear Injections
- How Cortisone is Injected into the Eardrum
- Indications for Cortisone Injections
- Causes of Perichondritis
- Symptoms of Perichondritis
- How Is Perichondritis Treated?
- How to Prevent Perichondritis?
- What If You’re Already Infected?
Benefits of Cortisone Ear Injections
- Pain relief: Alleviates ear pain caused by infections or other internal issues.
- Anti-inflammatory action: Cortisone acts as a potent anti-inflammatory agent, reducing swelling and irritation in the middle or inner ear, promoting overall ear health.
- Immune modulation: Suppresses immune reactions that might harm the inner ear, thus preventing potential damage.
- Rapid results: Provides fast and effective improvement in hearing-related issues.
- Prevents progression: Helps halt the progression of hearing problems associated with chronic or acute conditions, aiding in the preservation of auditory function.
How Cortisone is Injected into the Eardrum
The procedure of injecting cortisone into the tympanic membrane is a delicate one, performed in a clinical setting by specialized physicians. The process includes the following steps:
- The patient is positioned to ensure the affected ear is accessible for examination.
- The physician examines the eardrum using a medical microscope equipped with a light source for enhanced visibility.
- A local anesthetic is administered via ear drops to numb the area and reduce discomfort.
- A small perforation is made in the eardrum using a fine needle to facilitate drug delivery.
- Cortisone is injected through the same needle into the middle ear space.
- The patient must remain still—avoiding actions like swallowing or speaking—for approximately 45 minutes to ensure proper absorption of the medication.
Indications for Cortisone Injections
Cortisone injections are typically used with caution and are often considered a second-line treatment when oral or intravenous medications fail, though in some cases, they may be used in conjunction with other treatments or even as a first-line option. Common indications include:
Meniere’s Disease
A chronic condition characterized by episodes of severe vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Over time, the hearing may progressively worsen.
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SSNHL)
A rapid-onset hearing loss that typically occurs over a span of up to three days due to damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve. Immediate medical intervention is crucial to prevent permanent hearing loss.
Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease (AIED)
A rare disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the inner ear, leading to progressive hearing loss, tinnitus, and balance disturbances.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Cortisone injections may also be used in cases where hearing is affected by continuous exposure to loud noises, such as in industrial environments, helping prevent further auditory damage.
Side Effects and Risks of Cortisone Ear Injections
Although complications from cortisone ear injections are rare, some mild and temporary side effects may occur. If ignored, they could potentially lead to more serious issues. Possible side effects include:
- Headache
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Temporary hearing loss
- Tinnitus
- Numbness in the tongue
- Pain at the injection site
Serious Potential Complications
- Perforation of the tympanic membrane, which can negatively affect hearing.
- Burning sensation in the ear
- Risk of infection
- Ear fullness
- Fainting
- Ossicular chain weakening (leading to conductive hearing issues)
- Weight gain (in rare systemic absorption cases)
Cortisone ear injections offer a significant treatment option for individuals suffering from inner ear disorders, providing a chance for rapid and effective improvement in hearing. Maintaining good ear health, avoiding harmful auditory environments, undergoing regular check-ups, and consulting a specialist upon experiencing unusual symptoms are crucial steps toward preserving hearing and preventing complications.