Ear Infection
Ear infection, also known as otitis media, is one of the most common types of infections, particularly in children. It occurs due to a viral or bacterial infection that reaches the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the lower part of the throat. While some cases may resolve without treatment, others may require pain relievers, and more severe cases might need antibiotics under a doctor’s supervision.
In this article, we will explore the types, causes, symptoms, complications, and prevention methods of ear infection in both children and adults. Read on to learn more.
What is the Trachea’s Role in the Respiratory System?
The trachea acts as a link between the upper and lower respiratory tracts. At its end, it divides into two bronchial tubes—called bronchi—that connect the trachea to the lungs.
- Types of Ear Infection
- Causes of Ear Infection
- Symptoms of Ear Infection
- Complications of Ear Infection
- Preventive Measures Against Ear Infection
- When to See a Specialist
Types of Ear Infection:
There are three main types of ear infection:
Acute Otitis Media: This type occurs suddenly and is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling, redness, and intense ear pain.
Otitis Media with Effusion: Occurs after the initial infection clears, but fluid remains trapped in the ear, leading to a sensation of fullness and hearing difficulty.
Chronic Otitis Media: Results from unresolved issues like recurring infections or a persistent perforation in the eardrum.
Causes of Ear Infection:
Ear infection can be triggered by several factors, including:
Respiratory infections that spread to the ears due to Eustachian tube blockage, causing fluid to collect behind the eardrum—creating an environment for bacterial growth
Illnesses such as the flu, sinus infections, or throat inflammation that allow bacteria to travel to the Eustachian tube and cause swelling
Smoking, which increases the risk of respiratory and subsequently ear infections
In children, narrow Eustachian tubes and weaker immune systems make them more susceptible—especially during colds or allergies
- Bottle-fed babies are more prone to infection than those who are breastfed, particularly when fed while lying down
Symptoms of Ear Infection:
In Children:
Because ear infection is so prevalent in children, typical symptoms include:
Excessive crying
Loss of balance
Reduced appetite
Ear scratching or pulling
Fever
Yellow, sticky discharge from the ear
A feeling of pressure or blockage leading to hearing difficulties
- Sleep disturbances or sleeping excessively
In Adults:
Symptoms are similar but can be more defined, including:
Mild to severe ear pain
Irritability and discomfort
Difficulty sleeping
Discharge from the ear
Pressure in the ear and hearing problems
Nausea and vomiting
Dizziness and imbalance
Complications of Ear Infection:
Most ear infections resolve without complications, but frequent or untreated infections may lead to:
Hearing loss
Speech delays in children
Spread of infection between ears
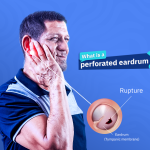
Eardrum perforation
Preventive Measures Against Ear Infection:
Here are some tips for preventing ear infections, especially in adults:
Avoid smoking, as it can irritate the respiratory tract and lead to ear infections
Keep ears clean and dry externally
Avoid using cotton swabs or objects to clean inside the ears, which may damage the ear canal or eardrum
Practice frequent hand washing to reduce germ transmission
Ensure children receive their routine vaccinations
- Encourage breastfeeding; if bottle-feeding, keep the baby upright during feeding
When to See a Specialist:
Treatment varies depending on the type of ear infection, but you should consult a doctor if the pain persists or symptoms last more than a day. It’s especially important to see a pediatric ENT if symptoms appear in infants under six months, particularly if accompanied by unexplained sleep disturbances.