Eustachian Tube Blockage
Eustachian Tube Blockage is like a hidden disruption in the secret bridge that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx. When this tube gets blocked, the smooth journey through the world of hearing becomes tiring and uncomfortable. But what exactly is eustachian tube blockage? What are its symptoms, causes, and how can it be treated? Let’s explore this troubling and bothersome condition together.
- What is eustachian tube blockage?
- Symptoms of eustachian tube blockage
- Causes of eustachian tube blockage
- Treatment Options for eustachian tube blockage
- Tips for Preventingeustachian tube blockage
What is eustachian tube blockage?
The Eustachian tube is a narrow canal that links the middle ear with the nasopharynx. It plays a crucial role in:
- Draining fluid from the middle ear.
- Equalizing pressure between the middle ear and the external environment.
- Protecting the ear from infections.
When the tube becomes blocked or inflamed, its normal functions are disrupted, leading to a condition known as Eustachian Tube Congestion, which can result in several auditory problems.
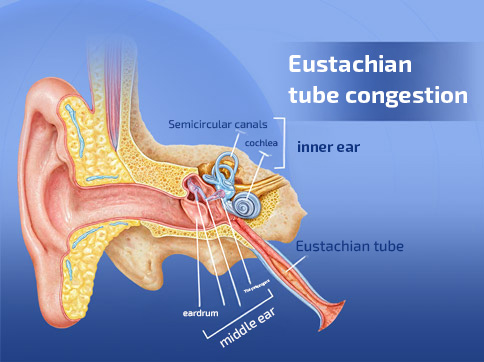
Symptoms of eustachian tube blockage
Individuals suffering from Eustachian Tube Dysfunction due to congestion may experience the following symptoms:
- Ear pain, especially during air travel or diving.
- A sensation of fullness in the ear.
- Temporary hearing loss or muffled sounds.
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears).
- Dizziness or balance issues.
Causes of eustachian tube blockage
Several factors can lead to eustachian tube blockage, including:
- Ear infections, which are among the most common causes, particularly in children.
- Sinus infections, which may cause swelling in the tissues surrounding the Eustachian tube.
- Allergies, which can inflame the mucous lining of the tube and lead to blockage.
- Atmospheric pressure changes, such as during flying or scuba diving.
- Benign tumors in the nose or throat, which may obstruct the Eustachian tube.
Treatment Options for eustachian tube blockage
The treatment of Eustachian Tube Congestion depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, the congestion may resolve on its own. However, general treatment options include:
- Medications, such as antibiotics, to treat associated ear or sinus infections.
- Decongestants, which can help reduce tissue swelling around the Eustachian tube.
- Nasal sprays, including saline or corticosteroid sprays, to relieve nasal congestion.
- Breathing maneuvers, such as the Valsalva maneuver, which can help open the Eustachian tube.
- Surgery, which may be necessary in rare cases to remove blockages or insert ear tubes.
Tips for Preventing eustachian tube blockage
To avoid developing Eustachian Tube Congestion, consider the following preventive measures:
- Promptly treat ear and sinus infections to prevent them from progressing and affecting the Eustachian tube.
- Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke, as they can irritate the Eustachian tube lining.
- Use ear protection while swimming to prevent water from entering the ear canal.
- Avoid flying or diving during a cold or nasal congestion.
- Regularly rinse the nasal passages with saline solutions to maintain sinus health.