Gastroesophageal Reflux
Gastroesophageal Reflux, also known as acid reflux, is a common medical condition that occurs when stomach acids flow back from their natural path into the esophagus. This can lead to a burning sensation in the chest and acidity.
In some cases, the reflux may intensify, allowing stomach acids to reach the trachea, causing inflammation that may even extend to the sinuses. But how does this happen? That’s what we’ll explore in the following lines.
- Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux
- Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux
- What Is the Relationship Between Gastroesophageal Reflux and Sinusitis?
- Gastroesophageal Reflux and Tinnitus: What’s the Connection?
- Preventing Gastroesophageal Reflux
- How to Treat Sinusitis Caused by Gastroesophageal Reflux?
Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux
There are several common symptoms experienced by those affected by Gastroesophageal Reflux, such as:
Burning sensation in the chest that may extend to the throat
Laryngitis
Dry cough and hoarseness
Difficulty swallowing
Feeling of a lump in the throat
In some cases, acid reflux can reach the pharynx and trachea, leading to the following symptoms:
- Nasal congestion
- Sour taste in the mouth with bad breath
- Shortness of breath due to acid reflux
- It may extend to the Eustachian tube and ears
- In some cases, it may cause ear ringing (tinnitus)
Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux
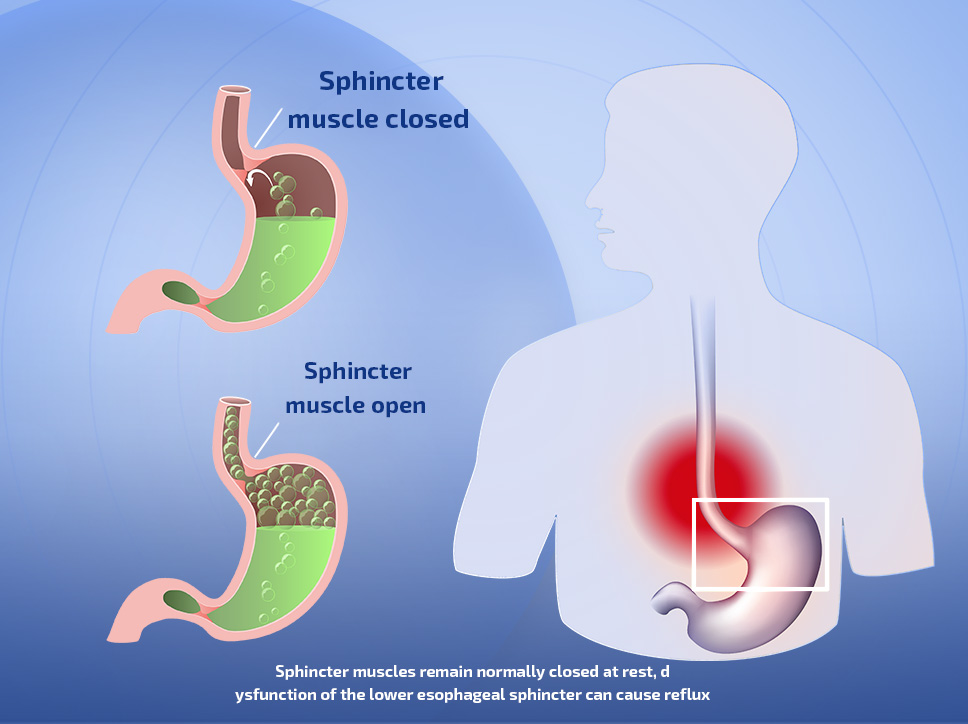
Medical specialists attribute Gastroesophageal Reflux to weakened muscles surrounding the lower part of the esophagus. These muscles control the passage of food and liquids into the stomach. Ideally, they relax to allow passage and then close tightly again.
If these muscles become loose, stomach acid may flow backward into the esophagus, causing inflammation of its inner lining and a burning sensation. A condition called hiatal hernia (diaphragmatic hernia) can also be a cause.
What Is the Relationship Between Gastroesophageal Reflux and Sinusitis?
Some might be surprised to learn about the link between Gastroesophageal Reflux and sinusitis. However, researchers have confirmed this connection. In severe cases of reflux, especially during sleep at night, stomach acids can continue to ascend through the esophagus to the larynx and eventually to the sinuses.
This causes inflammation of the nasal mucous membranes, impairing their protective function against smoke and harmful particles, and leading to chronic sinus allergies.
If you want to know more about sinusitis, its symptoms, and treatment methods, click here.
Gastroesophageal Reflux and Tinnitus: What’s the Connection?
Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux may experience ear pain and hearing difficulty due to inflammation of the Eustachian tube. This tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx and helps equalize air pressure in the middle ear.
It also drains fluids and secretions to the nasopharynx, preventing buildup inside the middle ear. When these secretions accumulate, the Eustachian tube can become blocked, leading to middle ear infections.
Sometimes, stomach acids passing through the round window membrane to the middle ear can damage the membrane, causing dizziness and a ringing sound in the ear.
If you’d like to learn more about the Eustachian tube and everything related to it, click here.
Preventing Gastroesophageal Reflux
There are some simple steps that can help prevent Gastroesophageal Reflux:
Avoid lying down immediately after eating
Avoid high-fat foods that increase stomach acid production
Avoid spicy foods
Refrain from smoking
Do not engage in physical activity or exercise immediately after eating
How to Treat Sinusitis Caused by Gastroesophageal Reflux?
To ensure accurate diagnosis and proper treatment, the doctor will conduct necessary tests and ask the patient several questions to determine whether sinusitis is caused by Gastroesophageal Reflux.
If so, treatment should begin with a consultation with a gastroenterologist to address the root cause. If sinus issues or tinnitus persist after reflux treatment, an ENT specialist will need to intervene.