Respiratory infections
Respiratory infections are considered one of the health problems that affect individuals of all ages, these infections can range from mild ones, such as the common cold, to more complicated and dangerous ones, such as pneumonia, these infections tend to increase during certain times of the year, especially in winter, when viruses and bacteria spread more rapidly, environmental factors like air pollution and smoking also play a significant role in increasing the risk of infection.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of respiratory infections, explaining their causes, symptoms, and how to prevent and treat them, the goal is to understand this health issue that affects millions of people worldwide and how to address it effectively.
- First: Upper Respiratory Infection
- Causes of Upper Respiratory Infections
- Symptoms of upper respiratory infections
- Types of upper respiratory infections
- Treatment of upper respiratory infections
- Prevention of upper respiratory infections
- Second: lower respiratory tract infections
- Causes of lower respiratory tract infections
- Types of lower respiratory tract infections
- Symptoms of lower respiratory tract infections
- Treatment of lower respiratory tract infections
- Prevention of lower respiratory tract infections
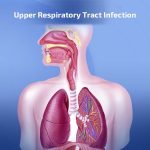
First: Upper Respiratory Infection
These are infections that affect the nasal passages, pharynx, and larynx, they are among the most common types of respiratory infections and are commonly known as the common cold. These infections occur frequently, especially during seasonal transitions, the infection may also include more severe conditions, such as pharyngitis and laryngitis.
Causes of Upper Respiratory Infections
Viral infections
Viruses are the leading cause of most respiratory infections, especially those affecting the upper respiratory tract. Common culprits include rhinoviruses, coronaviruses (like COVID-19), and adenoviruses. These viruses are highly contagious, spreading through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing—particularly in crowded or enclosed spaces.
Bacterial Infections
Although bacterial infections are less frequent than viral ones, they remain a significant factor in upper respiratory infections, Streptococcus pyogenes is one of the most common bacteria that cause throat infections and is the primary cause of pharyngitis,in some instances, it can lead to serious complications such as tonsillitis.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a large role in increasing the risk of infection, air pollutants, along with constant exposure to airborne contaminants like pollution smoke or cigarette smoke, can weaken the airways, making them more susceptible to infection. Additionally, exposure to allergens such as chemicals can further heighten the risk of developing these infections.
Symptoms of upper respiratory infections
Distinguishing between the symptoms of upper and lower respiratory infections is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Symptoms may vary depending on the type and severity of the infection, and can include the following:
Nasal congestion and runny nose
This occurs due to inflammation of the nasal passages and increased mucus secretion, it may lead to difficulty breathing through the nose and a feeling of nasal blockage.
Sore throat and cough
Often accompanied by a persistent and irritating cough, this can cause throat irritation, leading to discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
Fever and fatigue
Fever, along with fatigue, are signs of the body’s response to infection. The fever can range from mild to moderate.
Headache and body aches
Body aches and headaches may appear as part of the inflammatory response caused by the immune system fighting the infection, the intensity can vary from mild to severe.
Sneezing and watery eyes
Frequent sneezing and watery eyes are common symptoms that accompany upper respiratory tract infections, especially when the body reacts to viruses or irritants.
Types of upper respiratory infections
Common Cold
The common cold is one of the most frequent upper respiratory infections, leading to symptoms like nasal congestion, sore throat, and persistent coughing. It is typically caused by rhinoviruses, which spread easily from person to person, especially during the colder months.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is an inflammation that affects the air cavities located behind the nose and eyes, leading to facial pain, nasal congestion, and thick nasal discharge.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis, or sore throat, is characterized by swelling and redness in the throat, which causes pain and difficulty swallowing, it can be caused by a viral infection, such as the flu, or by bacteria like Streptococcus pyogenes, which is one of the most common bacterial causes of this condition.
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the upper respiratory tract that leads to hoarseness or complete loss of voice, this inflammation often results from a viral infection and may cause difficulty speaking or breathing in advanced cases.
Treatment of upper respiratory infections
Home remedies
There are several home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms, such as:
- Warm, Moist Air: It is recommended to expose yourself to steam by taking a hot shower or placing a warm towel on your face.
- Saline nasal solution: This can be used to reduce congestion, either by purchasing it from a pharmacy or preparing it at home.
- Warm liquids: Drinking warm beverages like tea or herbal drinks helps soothe the throat.
- Rest: Getting adequate rest is essential to boost the body’s ability to fight the infection.
- Avoiding smoking: To prevent irritation of the nose and throat.
Medications
There are several over-the-counter medications that can effectively relieve symptoms and support the treatment of upper respiratory infections. These include:”
Pain relievers
Decongestants
Allergy medications
Prevention of upper respiratory infections
To reduce the risk of developing upper respiratory tract infections, follow these preventive measures:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and frequently using soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Use tissues to cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and dispose of them immediately.
- Clean frequently-touched surfaces daily.
Eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly. - Get adequate rest and sleep.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who are infected.
- Do not share eating utensils with others.
Second: lower respiratory infections
These are bacterial or viral infections that affect the tissues and cells in the deeper parts of the respiratory system, such as the bronchioles and lungs, these infections are more serious than upper respiratory tract infections and may require immediate treatment to prevent complications later on.
Causes of lower respiratory tract infections
- Bacteria: Examples include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
- Viruses: Examples include the influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), parainfluenza virus, and human metapneumovirus.
- Exposure to Irritants and Allergens: Such as vapors, smoke, tobacco, dust, pollution, and chemicals.
Types of lower respiratory tract infections
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that affects the air sacs in the lungs, causing fluid or pus to accumulate, leading to symptoms such as coughing, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to an increase in mucus production and coughing, acute bronchitis is usually viral and resolves on its own, while chronic bronchitis results from prolonged exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke.
Bronchiolitis
Bronchiolitis is an infection that affects the small airways in the lungs, often occurring in children due to viral infections like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Common symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing.
Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs. Common symptoms include a persistent cough, chest pain, coughing up blood, weight loss, and night sweats.
Symptoms of lower respiratory tract infections
The symptoms of lower respiratory tract infections can vary based on the location and severity of the infection. They include:
Bronchitis
- Persistent cough, which may be accompanied by mucus in
- cases of chronic inflammation
- Shortness of breath or increased breathing rate in chronic cases
- Mild fever with a feeling of warmth
- Wheezing or whistling sounds during breathing
Bronchiolitis
- Cough and cold at the onset of the infection
- Restlessness and difficulty sleeping
- Snoring and wheezing when breathing
- Recurrent fever
- Increased breathing rate
Pneumonia
- Chest pain, worsening with breathing
- Irregular heart rate
- Fever and shortness of breath
- Headache and nausea
- Cough with mucus
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Persistent cough with blood in sputum
- Shortness of breath and fatigue
- Chest pain with ongoing fever
- Night sweats and weight loss
- Loss of appetite
Treatment of lower respiratory tract infections
The methods of treating lower respiratory tract infections vary depending on the underlying cause of the infection and its severity.
Home treatment
Some lower respiratory tract infections resolve on their own without the need for treatment, but less severe infections can be managed at home through:
- Over-the-counter medications for cough or fever.
- Drinking plenty of fluids.
- Adequate rest.
Medical treatment
A doctor may prescribe additional treatment, such as:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Breathing treatments, such as inhalers or nebulizers.
Hospital treatment
In some cases, the person may need to visit the hospital to receive:
- Intravenous fluids.
- Mechanical ventilation (if needed).
- Antibiotics.
Prevention of lower respiratory tract infections
- Preventive vaccinations
- Quitting smoking
- Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces
- Personal hygiene and regular handwashing
- Avoid direct contact with infected individuals
Respiratory tract infections are common health issues that can significantly affect our lives, however, thanks to medical advancements, it is now possible to prevent and treat them effectively, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can greatly reduce the risk of complications. Therefore, maintain the health of your respiratory system and be sure to consult a doctor if any symptoms appear for prompt diagnosis and treatment.