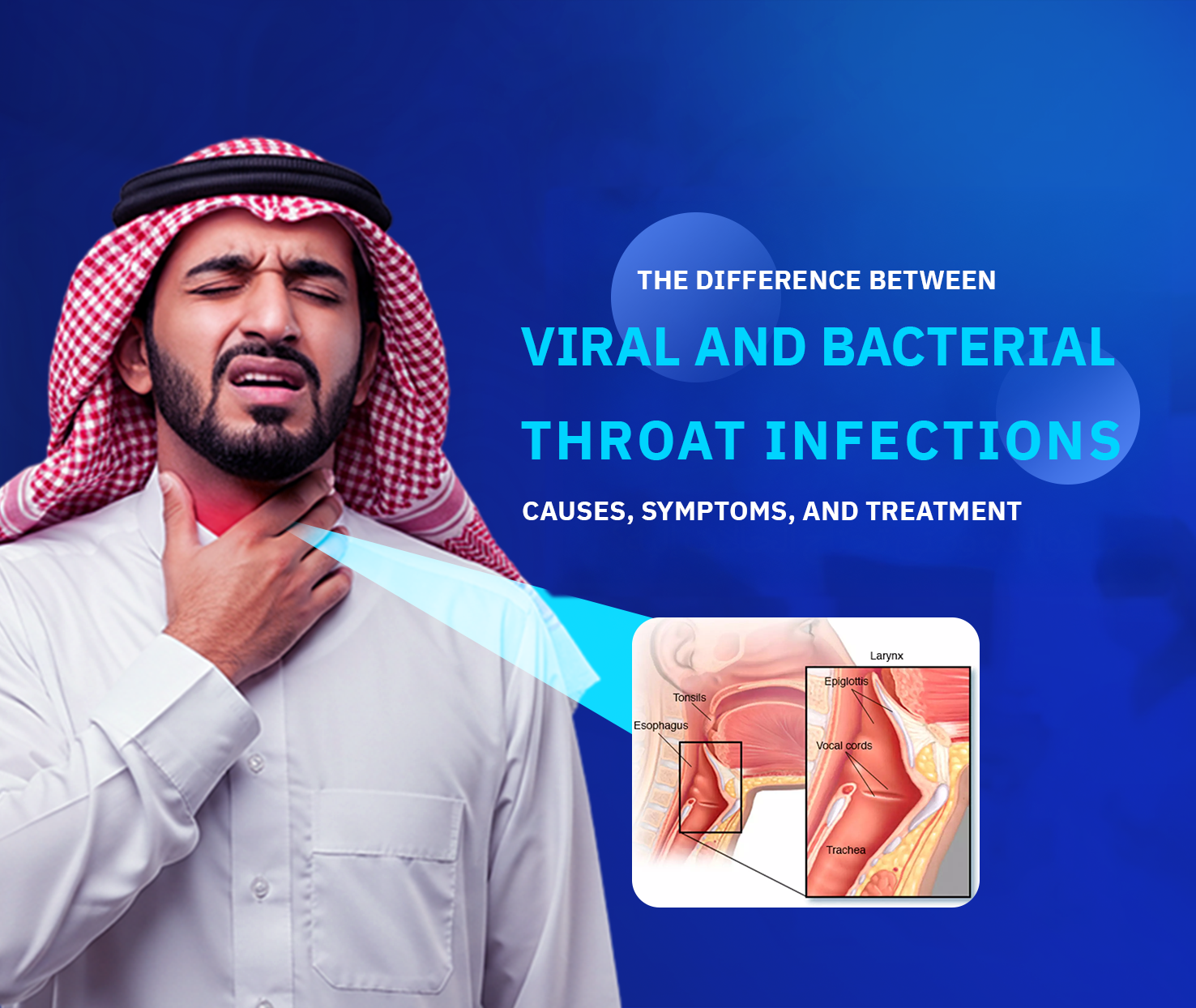
The Difference Between Viral and Bacterial Infections
The Difference Between Viral and Bacterial Infections is a common concern for those experiencing sore throat. Have you ever wondered if it’s caused by a virus or bacteria?
Understanding the difference between viral and bacterial throat infections is important, as symptoms may seem similar at first, but treatment varies significantly depending on the cause. That’s why recognizing the difference is key to effective prevention and care.
In this article, we’ll explore how to tell them apart, possible complications, and the best treatment options.
- The Difference Between Viral and Bacterial Infections
- Differences in Symptoms: Viral vs. Bacterial Infection
- Diagnosis of Viral and Bacterial Infections
- Treatment and Prevention of Viral and Bacterial Infections
- Complications of Viral and Bacterial Infections
- How Viral and Bacterial Infections Spread
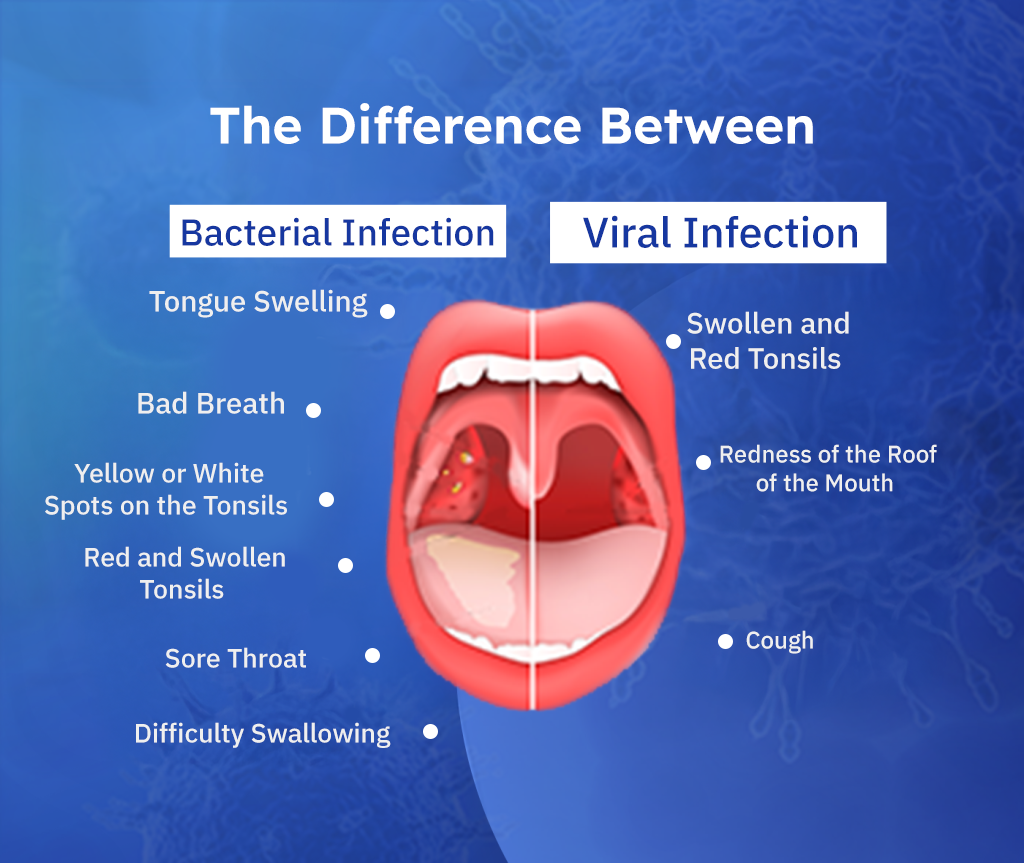
The Difference Between Viral and Bacterial Infections
Bacterial Throat Infection
Bacterial throat infections are commonly caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, which is why this condition is often referred to as “strep throat.” These bacteria are naturally found in the nose and throat.
This condition is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets released during coughing or sneezing, or by touching contaminated surfaces. Strep throat typically causes severe throat pain and difficulty swallowing and requires antibiotics for treatment.
Viral Throat Infection
Viral throat infections are caused by viruses such as those responsible for the common cold or influenza. These infections are also contagious and often lead to throat pain and congestion.
Unlike bacterial infections, viral sore throats do not respond to antibiotics. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms through rest, drinking warm fluids, and using over-the-counter pain relievers.
This condition is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets released during coughing or sneezing, or by touching contaminated surfaces. Strep throat typically causes severe throat pain and difficulty swallowing and requires antibiotics for treatment.
Differences in Symptoms: Viral vs. Bacterial Infection
Identifying the type of infection based on symptoms can help guide treatment. Below are the most common symptoms associated with each type:
Bacterial Throat Infection Symptoms
- Sudden fever (above 38°C / 100.4°F)
- Red, swollen tonsils with white patches
- Headache
- Pain when swallowing
- Stomach pain
- Nausea and vomiting (especially in children)
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Loss of appetite
Viral Throat Infection Symptoms
- Cough
- Throat swelling
- Mild pain while swallowing
- Low-grade fever
- Runny nose
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Headache
- Cough
Diagnosis of Viral and Bacterial Infections
Distinguishing between viral and bacterial infections is typically done using a rapid strep test, which involves a throat swab and provides results within five minutes.
Alternatively, a throat culture can be performed by collecting a sample from the throat and allowing any bacteria to grow in a lab setting for more accurate diagnosis.
Treatment and Prevention of Viral and Bacterial Infections
Accurate diagnosis is crucial as treatment methods differ significantly.
Home Treatment for Bacterial Throat Infections
- Gargling with warm salt water to soothe the throat
- Taking pain relievers to reduce pain and fever
- Using throat lozenges to reduce dryness and itching
- Drinking warm fluids like herbal teas and soups
- Getting plenty of rest to aid recovery
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Eating soft foods that are easy to swallow
Medical Treatment for Bacterial Throat Infections
Antibiotics should only be used under a doctor’s supervision and when the infection is confirmed as bacterial—especially in high-risk patients (e.g., those with heart disease, fever, weakened immune systems, or recurrent strep throat).
Home Treatment for Viral Throat Infections
- Gargling with salt water or antiseptic solutions like Betadine
- Using lozenges with vitamin C and topical analgesics
- Staying well-hydrated
- Inhaling steam with peppermint oil
- Drinking warm beverages like lemon-mint tea or broth
- Sleeping with the head elevated to help with mucus drainage
Medical Treatment for Viral Throat Infections
Anti-inflammatory medications may be used for severe symptoms, but antibiotics should not be used, as they are ineffective against viral infections. Misusing antibiotics can contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Complications of Viral and Bacterial Infections
Complications of Bacterial Throat Infections
If left untreated, strep throat can lead to serious complications:
- Sepsis: Infection entering the bloodstream, leading to body-wide inflammation
- Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the kidneys following strep infection
- Bacterial sinusitis: Causing facial pressure and congestion
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Guttate psoriasis: Often triggered in children
- Rheumatic fever
Complications of Viral Throat Infections
While typically less severe, viral infections can also cause complications:
- Ear infections
- Sinusitis
- Rheumatic fever (rare)
How Viral and Bacterial Infections Spread
Both types of infections spread in similar ways, including:
- Respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing
- Direct contact with infected individuals
- Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face
- Being in crowded places
- Contact with infected pets or insects
A sore throat can be a nuisance, but identifying whether it’s viral or bacterial is essential for proper treatment and a faster recovery. Regardless of the cause, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.